The first presentation focused on the “Sustainability of CBRNe Defense Programs in Low and Medium Income Countries (LMIC).” The second presentation chronicled Georgia’s experience addressing nuclear smuggling. For more information on Intersect Insight’s activity in these and related areas, see www.intersectinsight.com.
CSCM Congresses are dedicated to preventing the spread of knowledge and technology concerning weapons of mass destruction (WMD), specifically, those associated with chemical-biological-radiological-nuclear-explosives (CBRNe).
Mason’s presentations were based on our team’s involvement with the biosurveillance, public health program and CBRN defense planning in the country of Georgia, and our support to research activities at British and Ukrainian nuclear institutes. International donors from the developed world have supported the creation of CBRNe defense programs, first in the Former Soviet Union (FSU), and subsequently in an ever-widening number of developing countries. Intersect Insight recognizes the importance of their contributions and is dedicated to supporting the sustainability of these programs.
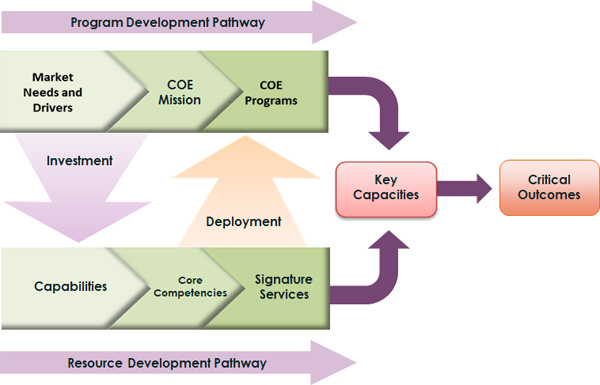
Much of the CBRNe effort has been focused on centers of excellence:
- Chemical, Biological, Radiological, and Nuclear (CBRN) are the major components comprising the concept of Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD)
- Many countries and several international donor programs have set up major activities to develop and indigenize the capability and capacity to counter a variety of threats to CBRN security. Much of that capacity is being created within a National Centers of Excellence (COEs) framework among LMIC countries
- COEs function as focal points for idea generation, implementation of best practices, training, technology transfer, and threat evaluation and response.
- COEs can be stand-alone organizations or new programs within existing institutions.
There is concern that the proficiency and funding of CBRN defense programs will prove unsustainable if donor funding wanes:
- CBRN Centers of Excellence can benefit from a sustaining strategy that borrows from business, academic and international development perspectives.
- Multiple business models for COEs can be recognized.
- Donors, operators, customers and other stakeholders have distinct expectations and roles.
- Best practices and lessons learned are available from multiple sources serving a variety of institutional missions.